Publications
|
Chang YT, Lee YJ, Haque M, Chang HC, Javed S, Lin YC, Abramovitz J, Chin G, Khamis A, Raja R, Murai KK, Huang WH
Comparative analyses of the Smith-Magenis syndrome protein RAI1 in mice and common marmoset monkeys J Comp Neurol., 2024 Jan;532(1):e25589. doi: 10.1002/cne.25589.
|
|
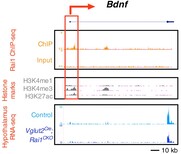
Javed S, Chang YT, Cho Y, Lee YJ, Chang HC, Haque M, Lin YC, Huang WH
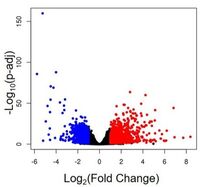
Smith–Magenis syndrome protein RAI1 regulates body weight homeostasis through hypothalamic BDNF-producing neurons and neurotrophin downstream signalling Elife, 2023 Nov 13:12:RP90333.
|
|
Chang HC, Lee YJ, Javed S, Haque M, Chang YT, Lin YC, Oram C, Huang WH
rAAV-CRISPRa therapy corrects Rai1 haploinsufficiency and rescues selective disease features in Smith-Magenis syndrome mice J Biol Chem., 2023 Jan;299(1):102728
|
|
Chang YT, Kowalczyk M, Fogerson PM, Lee JY, Haque M, Adams EL, Wang DC, DeNardo LA, Tessier-Lavigne M, Huguenard JR, Luo L, Huang WH
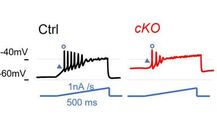
Loss of Rai1 enhances hippocampal excitability and epileptogenesis in mouse models of Smith-Magenis syndrome Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2022 Oct 25;119(43):e2210122119
|
|
Huang WH
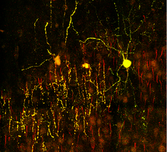
Performing Single Cell Clonal Analysis in the Mouse Brain using Mosaic Analysis with Double Markers (MADM) Methods Mol Biol., 2022 July;2515:59-74
|
|
Javed S, Lee YJ, Xu J, Huang WH
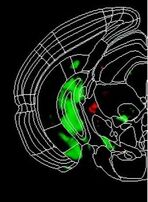
Temporal dissection of Rai1 function reveals brain-derived neurotrophic factor as a potential therapeutic target for Smith-Magenis Syndrome Hum Mol Genet., 2021 Dec 27;31(2):275-288
|
|
Javed S, Selliah T, Lee YJ, Huang WH
Dosage-Sensitive Genes in Autism Spectrum Disorders: From Neurobiology to Therapy Neurosci & Biobehav Rev., 2020 Nov;118:538-567
|
|
Luo L, Ambrozkiewicz MC, Benseler F, Chen C, Dumontier E, Falkner S, Furlanis E, Gomez AM, Hoshina N, Huang WH, Hutchison MA, Itoh-Maruoka Y, Lavery LA, Li W, Maruo T, Motohashi J, Pai ELL, Pelkey KA, Pereira A, Philips T, Sinclair JL, Stogsdill JA, Traunmuller L, Wang J, Wortel J, You W, Abumaria N, Beier KT, Brose N, Burgess HA, Cepko CL, Cloutier JF, Eroglu C, Goebbels S, Kaeser PS, Kay JN, Lu W, Luo L, Mandai K, McBain CJ, Nave KA, Prado MAM, Prado VF, Rothstein J, Rubesntein JL, Saher G, Sakimura K, Sanes JR, Scheiffele P, Takai Y, Umemori H, Verhage M, Yuzaki M, Zoghbi HY, Kawabe H, Craig AM
Optimizing Nervous System-Specific Gene Targeting with Cre Driver Lines: Prevalence of Germline Recombination and Influencing Factors Neuron, 2020 Apr 8;106(1):37-65.e5
|
|
Huang WH, Wang DC, Allen, WE, Klope M, Hu H, Shamloo M, Luo L
Early Adolescent Rai1 Reactivation Reverses Transcriptional and Social Interaction Deficits In a Mouse Model of Smith-Magenis Syndrome Proc Natl Acad Sci USA, 2018, Oct 16;115(42):10744-10749
|
|
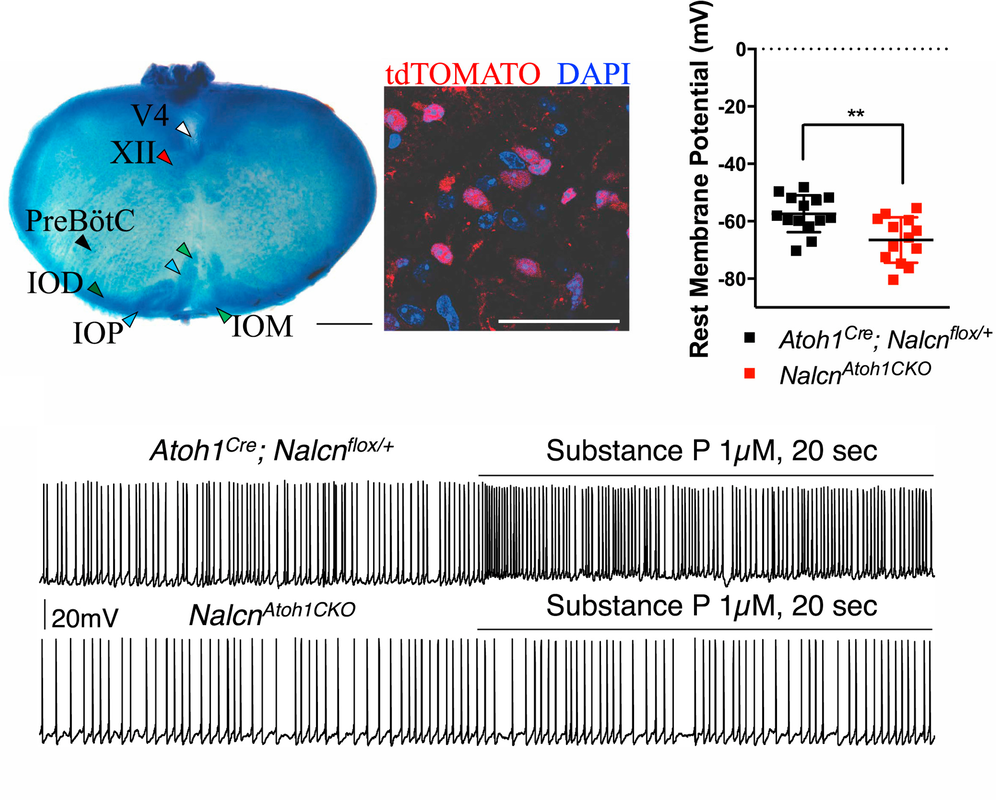
Yeh SY, Huang WH, Wang W, Ward CS, Chao ES, Wu Z, Tang B, Tang J, Sun JJ, van der Heijden ME, Gray PA, Xue M, Ray RS, Ren D, and Zoghbi HY
Respiratory network stability and modulatory response to substance P require Nalcn Neuron, 2017 Apr 19;94(2):294-303.e4
|
|
Huang WH, Guenthner CJ, Xu J, Nguyen N, Wilkinson AW, Gozani O, Chang HY, Shamloo M, Luo L
Molecular and Neural Functions of Rai1, The Causal Gene for Smith-Magenis Syndrome Neuron, 2016 Oct 19;92(2):392-406
|
|
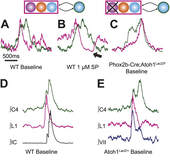
Tupal S, Huang WH, Picardo MC, Ling GY, Del Negro CA, Zoghbi HY, Gray PA
Atoh1-dependent rhombic lip neurons are required for temporal delay between independent respiratory oscillators in embryonic mice Elife, 2014 May 14;3:e02265
|
|
Huang WH, Tupal S, Huang TW, Ward CS, Neul JL, Klisch TJ, Gray PA, Zoghbi HY
Atoh1 governs the migration of postmitotic neurons that shape respiratory effectiveness at birth and chemoresponsiveness in adulthood Neuron, 2012 Sep 6;75(5):799-809
|